The Internet-of-Things (IoT) offers the potential to dramatically improve many tasks as diverse as preventative maintenance for electronic appliances to smart traffic lights to help reduce congestion.
As Pinakin Patel, head of Solutions Engineering for MapR says, many of the use cases require the collection of sensor data from edge devices that is sent over a network connection to a centralised application for analysis before an action is carried out; often back at the edge.
This classic input, process and output methodology is well understood but any IoT environment can be a data management challenge because of the huge volumes of data that are created and the latencies inherent in having global distribution.
Bigger IoT data
The challenges of aggregating data from consumer-oriented devices, like wearable technologies and smart thermostats, are well understood. For those types of devices, the volume of data is due to the large number of devices, and each individual device doesn’t necessarily create much data.
However, there are a new set of challenges for IoT devices that generate megabytes or gigabytes of data per second. For example, real time analysis of video, audio and ‘light detection and ranging’ (LIDAR) are all areas where the incoming streams could overwhelm traditional data storage architectures.
Certainly, the infrastructure will have to change, as those volumes of data will likely overwhelm the available bandwidth for aggregating the data into a central repository. Vehicles, medical devices, and oil rigs are perfect examples of sources of data that need a much more powerful architecture than those needed by consumer-oriented devices. And as these IoT data streams reach the centralised clouds for processing it will increasingly be Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning that will help to find insights and generate the subsequent actions.
Healthcare example
However, talking in the abstract when it comes to IoT it is difficult as each use case will have different drivers and requirements. Instead, let’s look at a few concrete examples as a proxy for the types of challenges that are involved.
The early detection and treatment of chronic diseases—such as heart disease can save lives and reduce the cost of healthcare. Two of the biggest issues are coordination of care and preventing hospital admissions for people with chronic conditions. Several trials are using cheaper sensors that can monitor patients’ vital signs and send this data along with Electrocardiogram (ECG) reading over cellular networks as a regular stream to applications in the cloud.
These diagnostic and monitoring applications analyse each patients’ vitals and ECG readings while considering historical data from medical records. The flows of data into the system include real-time streams, historical data, patient data and benchmark data created by aggregating huge volumes of previous scans from other patients.
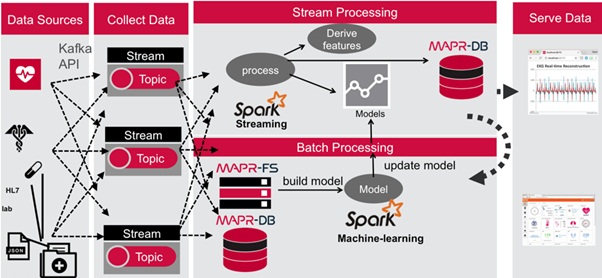
In this example, like many other within the IoT landscape, the clinicians require a workflow that collect data, aggregate, and learn across a whole population of devices to understand events and situations. In this scenario, the detection of an anomaly such as over medication or warning signs of an imminent cardiac event, may require more intelligence at the edge so they can react to those events very quickly.
The researchers have built a platform that uses common elements to process both stream and batch data within a common data fabric that can help handle all the data in the same way, control access to the data, and apply intelligence in a high performance and scalable fashion.
Automotive example
This data fabric approach is also being exported in other IoT applications. For example, Mojio — The IoT Connected Car aims to create an ecosystem that will allow the automotive, insurance, and telecom industry to thrive together. Mojio plans to connect 500,000 vehicles to its cloud platform in the first phase that will provide access to different types of behavioural, diagnostic, contextual data depending on need.
For example, behavioural data where Mojio’s telematics device gathers information about speed, steering, and braking inputs to determine a driver’s fatigue level and issue alerts. Long-term driving behaviour data can also be used to help the user adopt a more fuel-efficient driving style and calculate risk by insurance companies.
Convergence and fabrics
In both scenarios; the healthcare researchers and connected car engineers are examining new ways to build the next-gen apps. At the heart of these projects are several common technologies including cloud-scale data store to powerful database and integrated persisted streaming to create new possibilities for enterprise developers looking to architect, develop and deploy applications that were impossible until now.

The combination of these elements is often called a converged data platform and is starting to be adopted across a wider range of IoT use cases. These platforms provide benefits including the creation of a high IOPS, low latency file fabric for high performance computing apps. Another advantage is in real-time analytics scenarios where a data fabric can simultaneously ingest, store, analyse, process, and decide, without making copies.
As IoT data moves from the edge to the cloud and back again, organisations will need to forget the monolithic architectures of the past and consider convergence as the starting point to deliver the scale needed for innovative new use cases.
The author of this blog is Pinakin Patel, head of Solutions Engineering for MapR.
About the author
Pinakin Patel is the head of Solutions Engineering for MapR. He has more than 25 years of experience in the world of data and how organisations extract value from this critical business resource.
Comment on this article below or via Twitter: @IoTNow_OR @jcIoTnow










